前言
最近公司的一个业务需要使用Java操作Excel表格,于是去B站学习了以下两个框架
POI
常用操作
将用户信息导出为excel表格(导出数据….)
将Excel表中的信息录入到网站数据库(习题上传….)
开发中经常会设计到excel的处理,如导出Excel,导入Excel到数据库中!
操作Excel目前比较流行的就是 Apache POI 和 阿里巴巴的 easyExcel !
Apache POI
Apache POI 官网:https://poi.apache.org/

easyExcel
easyExcel 官网地址:https://github.com/alibaba/easyexcel
EasyExcel 是阿里巴巴开源的一个excel处理框架,以使用简单、节省内存著称。
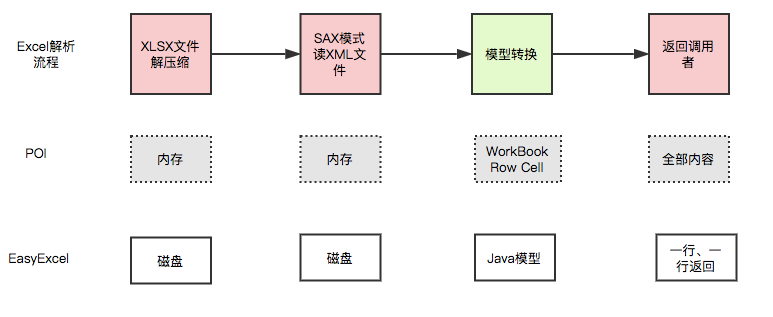
EasyExcel 能大大减少占用内存的主要原因是在解析 Excel 时没有将文件数据一次性全部加载到内存中,而是从磁盘上一行行读取数据,逐个解析。
下图是 EasyExcel 和 POI 在解析Excel时的对比图。
官方文档:https://www.yuque.com/easyexcel/doc/easyexcel
POI-Excel写
创建项目
1、建立一个空项目 ,创建普通Maven的Moudle kuang-poi
2、引入pom依赖
1 | <dependencies> |
03 | 07 版本的写,就是对象不同,方法一样的!
需要注意:2003 版本和 2007 版本存在兼容性的问题!03最多只有 65535 行!
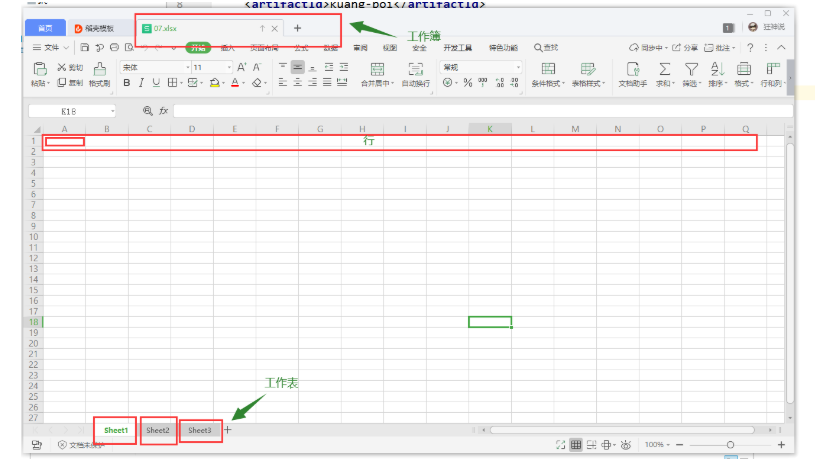
1、工作簿:
2、工作表:
3、行:
4、列:
03版本:
1 |
|
07版本:
1 |
|
注意对象的一个区别,文件后缀!
数据批量导入!
大文件写HSSF
缺点:最多只能处理65536行,否则会抛出异常
1 | java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Invalid row number (65536) outside allowable range (0..65535) |
优点:过程中写入缓存,不操作磁盘,最后一次性写入磁盘,速度快
1 |
|
大文件写XSSF
缺点:写数据时速度非常慢,非常耗内存,也会发生内存溢出,如100万条
优点:可以写较大的数据量,如20万条
1 |
|
大文件写SXSSF
优点:可以写非常大的数据量,如100万条甚至更多条,写数据速度快,占用更少的内存
注意:
过程中会产生临时文件,需要清理临时文件
默认由100条记录被保存在内存中,如果超过这数量,则最前面的数据被写入临时文件
如果想自定义内存中数据的数量,可以使用new SXSSFWorkbook ( 数量 )
1 |
|
SXSSFWorkbook-来至官方的解释:实现“BigGridDemo”策略的流式XSSFWorkbook版本。这允许写入非常大的文件而不会耗尽内存,因为任何时候只有可配置的行部分被保存在内存中。
请注意,仍然可能会消耗大量内存,这些内存基于您正在使用的功能,例如合并区域,注释……仍然只存储在内存中,因此如果广泛使用,可能需要大量内存。
再使用 POI的时候!内存问题 Jprofile!
POI-Excel读
03|07 版本
03版本
1 |
|
07版本
1 |
|
注意获取值的类型即可
读取不同的数据类型(最麻烦的就是这里了!)
1 |
|
注意,类型转换问题;
计算公式 (了解即可!)
1 |
|
EasyExcel操作
导入依赖
1 | <dependency> |
写入测试
https://www.yuque.com/easyexcel/doc/read
创建对象
1 |
|
拿到实体类里的值
1 | String PATH ="D:\\Project\\IdeaProject\\Java_work\\"; |
将list写入Excel
1 | // 根据list 写入excel |
读取测试
https://www.yuque.com/easyexcel/doc/read
对象
监听器
1 | // 有个很重要的点 DemoDataListener 不能被spring管理,要每次读取excel都要new,然后里面用到spring可以构造方法传进去 |
持久层
1 | /** |
测试代码
1 |
|
固定套路:
1、写入,固定类格式进行写入
2、读取,根据监听器设置的规则进行读取!一、POI

